

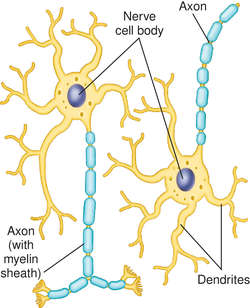
With their tremendous complexity and diversity, dendrites are one of nature’s architectural masterpieces.
#Define dendrite drivers#
Here, we review cell-intrinsic drivers of dendrite patterning and discuss how the characterization of such crucial regulators advances our understanding of normal brain development and pathogenesis of diverse cognitive disorders. In particular, studies in Drosophila and mammalian neurons have identified numerous cell-intrinsic drivers of dendrite morphogenesis that include transcriptional regulators, cytoskeletal and motor proteins, secretory and endocytic pathways, cell cycle-regulated ubiquitin ligases, and components of other signaling cascades. Although these developmental stages were characterized over a century ago, molecular regulators of dendrite morphogenesis have only recently been defined. Following cell cycle exit and migration, neurons undergo organized stages of dendrite morphogenesis, which include dendritic arbor growth and elaboration followed by retraction and pruning.
#Define dendrite professional#
As dendritic cells were relatively rare, itt took until the 1980’s for them t become accepted as professional APCs.The proper formation and morphogenesis of dendrites is fundamental to the establishment of neural circuits in the brain. Compared with dendritic cells, macorphages were present in much greater numbers, were evenly spread throughout the body and had were known to present antigens. Before this, immunologists generally thought that macrophages were the main APC in the immune system. He found these cells in the spleen and it was later discovered that the cells were present in all lymphoid and most non-lymphoid tissues. During development, they develop branched projections called “dendrites”, which is why the cells are so named.ĭendritic cells were first described by Ralph Steinman in the 1970’s. Once activated, dendritic cells move to the lymph tissue to interact with to interact with T cells and B cells and help shape the adaptive immune response. Immature forms are also found in the blood.
#Define dendrite skin#
This is to provide a long lasting source of antigen that the B cells can take up themselves and present to T cells.ĭendritic cells are found in tissue that has contact with the outside environment such as the over the skin (present as Langerhans cells) and in the linings of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. After an initial antibody response has occurred due to an invading body, dendritic cells found in the germinal centre of lymph nodes seem to contribute to B cell memory by forming numerous antibody-antigen complexes. Dendritic producing cytokines and other factors that promote B cell activation and differentiation. Measuring airway inflammation when diagnosing and treating asthma patientsĭendritic cells also contribute to the function of B cells and help maintain their immune memory.Study discovers how the immune system triggers an 'emergency' dendritic cell response during infection.MIT researchers uncover a possible new way to combat tumors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
